The difference between purple foods

According to experts, the health benefits of the natural pigments that provide the purple, red, and blue hues in fruits and vegetables are indisputable. "Anthocyanin, the mysterious force behind these colors, is a powerful component that supports our health," said Internal Medicine Specialist Prof. Dr. Osman Erk, explaining this distinctive feature of purple foods as follows:

They cooperateProf. Dr. Osman Erk
The power of purple isn't just due to anthocyanins. It's also linked to other phenolic compounds (quercetin, kaempferol, ellagic acid, punicic acid, resveratrol, pterostilbenes), vitamins, and minerals. All of these elements work together like a harmonious orchestra to produce significant health benefits. Organic fruits and vegetables contain more anthocyanins.
It fights cancerAnthocyanins prevent the formation and spread of cancer cells thanks to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Scientific studies have stated that blackberries and blueberries may have protective effects against common types of cancer such as breast, colon, prostate and lung cancer.
Dark raspberries have been shown to slow the development of cancer in colon polyps.
Health effects of anthocyanin Protects the heart and blood vesselsAnthocyanins lower blood pressure by increasing nitric oxide release, reduce clotting, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by preventing vascular inflammation and the oxidation of LDL cholesterol.
A 2008 scientific study proved the positive effects of blueberry consumption on platelet function, blood pressure, and HDL cholesterol.
It slows down the rate of agingAnthocyanins reduce oxidative stress by combating free radicals with their powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This antioxidant effect reduces the aging process and the risk of diseases caused by oxidative stress.
Protects against diabetesAnthocyanins prevent the development of diabetes. They reduce the activity of enzymes involved in carbohydrate absorption, slowing the formation and transfer of glucose into the bloodstream, thus preventing blood sugar spikes.
Increases good bacteriaAnthocyanins are found primarily in the intestines, improving barrier function and balancing the gut microbiota. They act as prebiotics, increasing the number of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Strengthens memoryAnthocyanins help prevent neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, etc.) by protecting the blood-brain barrier. Scientific studies have shown that anthocyanins increase memory and learning capacity.
Fruits and vegetables are rich in anthocyaninsPurple colored fruits and vegetables have high anthocyanin content.
Foods rich in anthocyanins include blackberries, blueberries, raspberries, grapes, black cherries, black carrots, prunes, eggplant, beets, purple cauliflower, purple kale, purple artichokes, purple potatoes, aronia, black mulberries, sour cherries, cranberries, strawberries, elderberries, and pomegranates. Anthocyanins are also found in plants like black rice, pollen, and sumac.
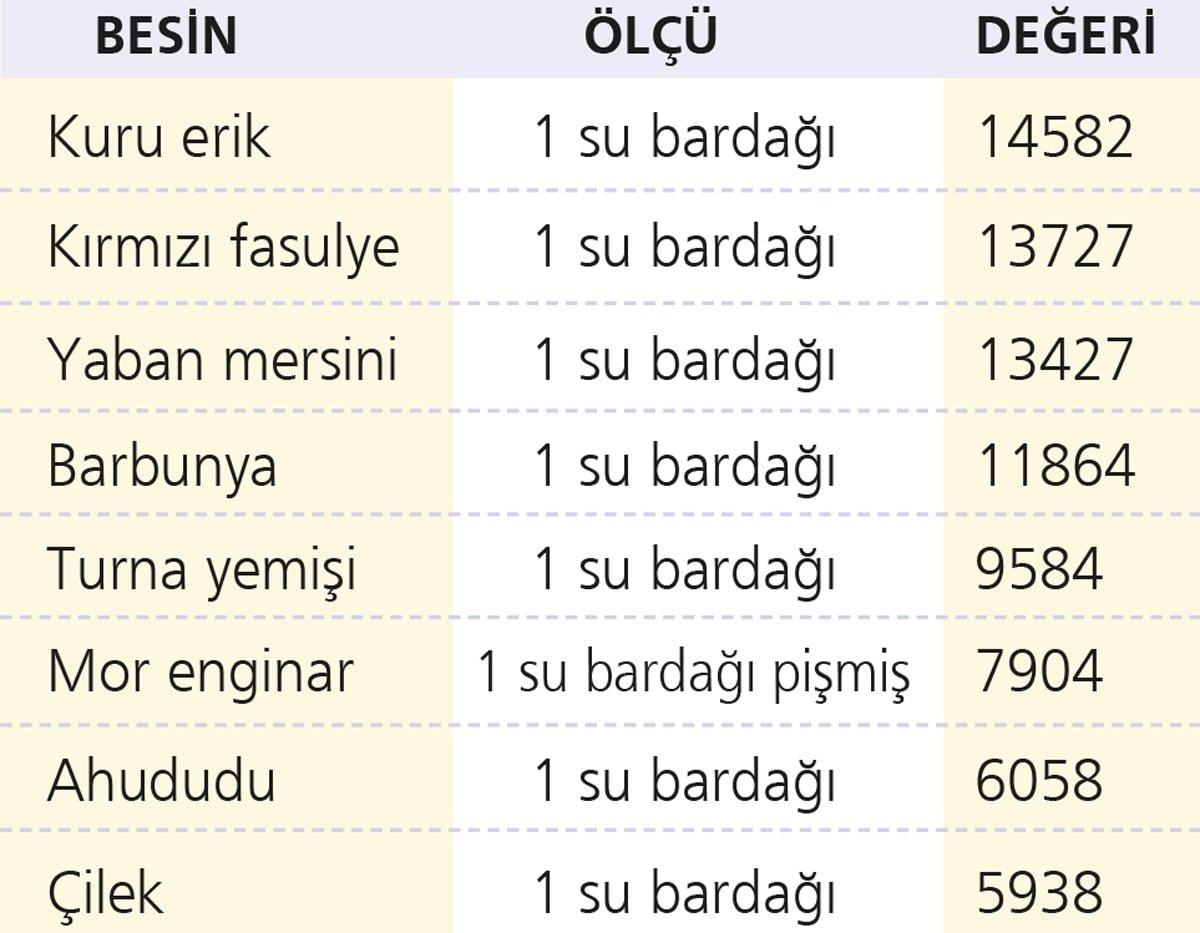
They have the highest ORAC valueORAC ranks antioxidant levels in foods. Here are some purple foods and their antioxidant levels:
Anthocyanins contribute significantly to the life cycle, adaptation, and reproductive strategies of plants. Harmful UV rays in sunlight cause DNA damage in plant tissues. Anthocyanins reduce this harmful effect and protect the plant.
Heat, cold, drought, humidity, wind, and harmful pathogens also create environmental stress for plants. Anthocyanins help plants adapt to stressful environmental conditions.
It has the same effect on humans.
Anthocyanins, just like plants, have protective effects in humans. They reduce toxin accumulation in the body by combating free radicals we are exposed to through air pollution and adulterated foods, as well as metabolic activity.
SÖZCÜ





